Difference between revisions of "What is an open value network?"
imported>TiberiusB |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''Open Value Network'' has the acronym ''OVN''. | ''Open Value Network'' has the acronym ''OVN''. | ||
| − | '''From a social perspective''': an OVN is a complex form of social [[organization]]. Through interaction, values and rules as well as norms of reciprocity and trustworthiness are constantly emerging and being (or not) sustained. | + | '''From a social perspective''': an OVN is a complex form of social [[organization]]. Through interaction, values and rules, as well as norms of reciprocity and trustworthiness, are constantly emerging and being (or not) sustained. |
| − | '''From an economic perspective''': an OVN is a group of [[agents]] that collaborate openly and transparently to offer goods and services, expecting benefits in proportion to everyone’s [[contribution]] | + | '''From an economic perspective''': an OVN is a group of [[agents]] that collaborate openly and transparently to offer goods and services (valuables -see [[value]]), expecting [[benefits]] in proportion to everyone’s [[contribution]] -see [[NRP-CAS]]. |
| − | An OVN is understood as a [[complex dynamical system]], a [[living system]], with an emergent structure (not imposed or predefined). We are looking at ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autopoiesis, autopoetic]'' or ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organization, self-organizing]'' systems. There are '''initial conditions''' for such systems to exist and basic requirements for such systems to succeed in their mission, which are characterized as a [[Critical Path]]. | + | An OVN is understood as a [[complex dynamical system]], a [[living system]], with an emergent structure (not imposed or predefined). We are looking at ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autopoiesis, autopoetic]'' or ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organization, self-organizing]'' systems. There are '''initial conditions''' for such systems to exist and basic requirements for such systems to succeed in their mission (as [[agents]]), which are characterized as a [[Critical Path]]. |
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| − | It is the network that is open. | + | It is the ''network'' that is ''open''. |
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
* peer property - the use-value of property is accessible on a collective trust basis through new modes of ownership which are not exclusive, while recognizing individual authorship or title where appropriate. | * peer property - the use-value of property is accessible on a collective trust basis through new modes of ownership which are not exclusive, while recognizing individual authorship or title where appropriate. | ||
| − | Am OVN allows individuals to engage in economic activities | + | Am OVN allows individuals to engage in economic activities by pulling together various assets that they may possess, bypassing money for the most part. Data from [[Sensorica]] shows that the financial barrier to produce a hardware prototype through a [[collaborative venture]] can be reduced to 10% when compared to a traditional startup. In that sense, the OVN model is breaking away from the traditional ''transactional'' economy, which is over-dependent on financial assets: without money it is very hard to engage in economic processes, i.e. it is hard to launch a company, put a product on the market, without financial capital. |
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
An OVN is built on a [[value system]], as perceived by humans, composed of sources, processes of creation, production, reproduction processes, transformation, transmutation, exchange mechanisms,... all that embodied as a decentralized form of [[organization]]. | An OVN is built on a [[value system]], as perceived by humans, composed of sources, processes of creation, production, reproduction processes, transformation, transmutation, exchange mechanisms,... all that embodied as a decentralized form of [[organization]]. | ||
| − | : Some [[value systems]] are in most part abstractions. A cult or a sect is built on a [[value system]]. Apart from tangible benefits for being part of a tight group, a large part of the [[value system]] is purely immaterial, subjective and even illusory. The same can be said for a corporation or a cooperative, there are tangible benefits flowing through them as well as intangible benefits, real and imaginary. The benefits or the negative effects people get from engaging in different endeavors, either properly understood or not (in the case of deception), can be very real and tangible. | + | : Some [[value systems]] are in most part abstractions. A cult or a sect is built on a [[value system]]. Apart from tangible benefits for being part of a tight group, a large part of the [[value system]] is purely immaterial, subjective and even illusory. The same can be said for a corporation or a cooperative, there are [[tangible benefits]] flowing through them as well as [[intangible benefits]], real and imaginary. The [[benefits]] or the negative effects people get from engaging in different endeavors, either properly understood or not (in the case of deception), can be very real and tangible. |
| − | : What comes first, value or structure? I.e. what comes first, a [[role system]] or a [[value system]]? Is a [[value system]] determining the [[role system]] or vice versa? | + | : What comes first, [[value]] or structure? I.e. what comes first, a [[role system]] or a [[value system]]? Is a [[value system]] determining the [[role system]] or vice versa? We believe that [[value]] comes first, the [[value system]] should inform the [[role system]]. The structure of any [[organization]] depends on the nature of the flows through it. See also [https://docs.google.com/document/d/1OytVGkt56a8gaWs64a6Ggj8Sg4WZqo6VDDK0GcH2Kvc/edit?hl=en#heading=h.4g3fr3t9q03 here], the same ideas are expressed, if modified do it everywhere |
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
Moreover, the OVN is supported by an infrastructure that reduces transaction costs among peers. | Moreover, the OVN is supported by an infrastructure that reduces transaction costs among peers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: [[Sensorica]] has moved past this narrative where the ''market'' has a lesser role. For example, the [https://www.sensorica.co/ventures/food-and-agriculture/greens-for-good Greens for Good venture] produces food processing equipment not as [[commodities]], but as [[open source]], [[DIY]] artifacts, i.e. designed for easy local manufacturing, by anyone, for any purpose. These artifacts are not sold as products on the open market. In other words, the distribution is not through [[market]] transactions, rather through a process of ''dissemination''. | ||
== Production and distribution == | == Production and distribution == | ||
| Line 98: | Line 100: | ||
=== Production === | === Production === | ||
| − | + | Is a participatory process, where almost everything is [[crowdsourced]]. Feeds on collective/social intelligence, relies on crowdthinking processes, uses much less [[planning]], uses [[stigmergy]]. | |
| − | + | Uses [[infrastructure]] for collaboration / co-production with transactional capabilities for various assets, under various [[property]] regimes, in order to unblock economic [[processes]] of design and production. Reduces transaction costs. | |
| − | Relies on a values | + | Relies on a system of values (motivation) and [[incentives]]. |
| − | === | + | === Dissemination === |
| − | + | The term ''dissemination'' has replaced ''distribution'' during 2021, with the [https://www.sensorica.co/ventures/food-and-agriculture/greens-for-good Greens for Good]] venture, to distinguish between market-based or transactional distribution of (scarce, rivalrous) commodities and dissemination of digital assets (abundant, non-rivalrous) such as open source designs. | |
== Characteristics == | == Characteristics == | ||
Revision as of 07:51, 8 April 2022
Open Value Network has the acronym OVN.
From a social perspective: an OVN is a complex form of social organization. Through interaction, values and rules, as well as norms of reciprocity and trustworthiness, are constantly emerging and being (or not) sustained.
From an economic perspective: an OVN is a group of agents that collaborate openly and transparently to offer goods and services (valuables -see value), expecting benefits in proportion to everyone’s contribution -see NRP-CAS.
An OVN is understood as a complex dynamical system, a living system, with an emergent structure (not imposed or predefined). We are looking at autopoetic or self-organizing systems. There are initial conditions for such systems to exist and basic requirements for such systems to succeed in their mission (as agents), which are characterized as a Critical Path.
Value and network
Value
See pages: Value and What is value?
Network
Means a set of interconnected autonomous agents who maintain a set of relations, dictated by their respective roles, and act according to a set of shared rules and methodologies. Agents are called affiliates in the OVN model.
The term network refers to the various structures within the OVN. It conveys the notion of free association. It also suggests a departure from hierarchies, to more dynamic structures, which might also contain contextual and ephemeral hierarchies, but not permanent instituted power relations. It also suggests a more horizontal governance, where choices or decisionmaking does not rely on specific nodes (positions or roles / occupied by agents), but is more inclusive and context dependent, based on the relation between nodes (roles that are dynamically occupied by agents) and the process at stake.
See technical definition of a network from WolframMatworld.
It is the network that is open.
As an environment for socioeconomic activity
The OVN environment provides value sovereignty to the agents that operate within it. In other words, autonomous agents or affiliates collectively decide in context how to link participation (or contributions) with distribution of benefits.
New economic model
OVN is an approach to commons-based peer production. It allows agents (individuals and organizations) to
- co-create and aggregate valuables through lateral and large scale coordination, cooperation and collaboration
- to steward of shared wealth and assets
- to account for various inputs and outcomes in a common ledger system
- distribute benefits fairly within and beyond the network, based on participation (or contributions or other considerations)
The OVN model relies on p2p principles of co-production, self-organization, and stewardship of commons.
- peer production - the collaborative production of surplus value by means of common and contributed assets;
- peer governance - direction and accountability by the community of producers themselves, not by market allocation or corporate hierarchy;
- peer property - the use-value of property is accessible on a collective trust basis through new modes of ownership which are not exclusive, while recognizing individual authorship or title where appropriate.
Am OVN allows individuals to engage in economic activities by pulling together various assets that they may possess, bypassing money for the most part. Data from Sensorica shows that the financial barrier to produce a hardware prototype through a collaborative venture can be reduced to 10% when compared to a traditional startup. In that sense, the OVN model is breaking away from the traditional transactional economy, which is over-dependent on financial assets: without money it is very hard to engage in economic processes, i.e. it is hard to launch a company, put a product on the market, without financial capital.
Organizational model
An OVN is a generic organizational model that can be implemented in different forms, adapted to specific contexts. It allows low-barrier access to innovation and co-creation processes, oriented towards economies of scope, as opposed to economies of scale.
An OVN is built on a value system, as perceived by humans, composed of sources, processes of creation, production, reproduction processes, transformation, transmutation, exchange mechanisms,... all that embodied as a decentralized form of organization.
- Some value systems are in most part abstractions. A cult or a sect is built on a value system. Apart from tangible benefits for being part of a tight group, a large part of the value system is purely immaterial, subjective and even illusory. The same can be said for a corporation or a cooperative, there are tangible benefits flowing through them as well as intangible benefits, real and imaginary. The benefits or the negative effects people get from engaging in different endeavors, either properly understood or not (in the case of deception), can be very real and tangible.
- What comes first, value or structure? I.e. what comes first, a role system or a value system? Is a value system determining the role system or vice versa? We believe that value comes first, the value system should inform the role system. The structure of any organization depends on the nature of the flows through it. See also here, the same ideas are expressed, if modified do it everywhere
From an agent perspective
- Equipotentiality: The assumption that all agents have the potential to satisfy requirements to contribute constructively to processes, thus, no one is excluded apriori.
- Anti-credentialism: The emphasis is put on what an agent can do, not on credentials, although credentials are considered in access to processes. If a process or a resource is not rivalrous and not sensitive (in terms of safety and security) barriers to access are very low, anyone can engage in the process or use the resource.
- Self-selection: Allow agents to chose their roles instead of being appointed to positions.
- Peer validation: Rely on peers rather than on authority to establish truth, quality, adequacy, etc.
- Holoptism: Provide unrestricted access to information to all agents
Other definitions
From Wikipedia. See our Diigo annotated version of this Wikipedia page.
See metamaps.cc definition short and metamaps.cc definition long
Applications
- High tech enterprise: Sensorica
- Exchange service: Bitcoin network
- Services
- Translation: Guerilla Translations
Application scenario in high tech
Imagine a mechanical engineer. We’ll call him Joe. Joe has a very good product-idea but he has very little money. Let’s also assume that in order to market Joe’s product-idea it would require the input from other individuals with complementary skills, like chemistry, electronics, sales and marketing, administration, etc.. In the traditional world, Joe would have a few options to bring his idea to market.
The first and most obvious option is based on an individualistic approach. Because Joe doesn’t have enough money, he must find the funds necessary to buy some tools, to rent a space, and to hire employees. If financiers are involved early on, they will rightfully ask for a larger share in the venture, in proportion to the greater risk they take (greater uncertainty).
A second option, where Joe would start by creating a partnership. He must find other individuals with complementary skills and convince them to join the venture. Remember, we are supposing that Joe doesn’t have enough money to hire other employees. Once the group is formed, Joe and his partners create a company, and they decide to each take a % of the company -equity. Within this secure environment (the company and its legal/contractual mechanisms) the partners share risk, they work together to grow the potential of their venture, enough to reach the threshold of confidence at which financiers would become interested to invest at lower risk. At that stage, the co-founders must agree to give a portion of their shares to the investors (to dilute), who will rightfully ask for a share in the venture in exchange of the risk they are willing to undertake. If investors get involved at a later stage, the percentage given to them might be smaller than in the first case.
How is that going to affect Joe’s bottom line? In fact, Joe can end up in almost the same place. But his friends/partners are now co-owners instead of being just employed by Joe, which is probably better, because they have a stake into the business and can be more motivated.
Imagine now that Joe can find not only a few partners, but thousands of them. In this case, the venture initiated by Joe might not even need financing at all, if all these partners bring with them no only skills and know how, but also different materials like tools and instruments, access to physical work spaces, and even a bit of cash. Finding thousands of partners in an effective amount of time was impossible 20 years ago, because we were limited to our social network within a small geographical area. Today, the Internet allows this possibility, if the idea is great and if Joe has the proper social skills.
In the second scenario, cooperation and sharing is involved. The OVN extends the second scenario to the point where there might not be a need to rely on financiers. It allows Joe to bring his idea to market entirely through sharing and collaboration. We already have examples to point to. GNU/Linux, the open source operating system, was entirely produced through cooperation by thousands of individuals, distributed throughout the planet. Wikipedia is another example of massive collaboration and co-production. We call that peer-production. The problem with these examples is that no revenue is generated. There are no direct tangible returns from this type of participation. These are called gift economies. An OVN goes beyond the gift economy. It actually contains a gift economy, but it allows those who participate in the production process to be rewarded in a tangible way. In other words, OVNs allow individuals to get involved and to initiate economic processes through sharing and collaboration, relying less on financial assets. Time, skills, tools, physical spaces, social capital, and other tangible or intangible assets can be used as currencies within the value network.
Moreover, the OVN is supported by an infrastructure that reduces transaction costs among peers.
NOTE: Sensorica has moved past this narrative where the market has a lesser role. For example, the Greens for Good venture produces food processing equipment not as commodities, but as open source, DIY artifacts, i.e. designed for easy local manufacturing, by anyone, for any purpose. These artifacts are not sold as products on the open market. In other words, the distribution is not through market transactions, rather through a process of dissemination.
Production and distribution
Production
Is a participatory process, where almost everything is crowdsourced. Feeds on collective/social intelligence, relies on crowdthinking processes, uses much less planning, uses stigmergy.
Uses infrastructure for collaboration / co-production with transactional capabilities for various assets, under various property regimes, in order to unblock economic processes of design and production. Reduces transaction costs.
Relies on a system of values (motivation) and incentives.
Dissemination
The term dissemination has replaced distribution during 2021, with the Greens for Good] venture, to distinguish between market-based or transactional distribution of (scarce, rivalrous) commodities and dissemination of digital assets (abundant, non-rivalrous) such as open source designs.
Characteristics
- Openness: barrier to entry for participation, access to resources
- Transparency access given to the public to information, processes
- Reliability: defines the reliability of the network components and the connectivity between them. Mean time between failures (MTBF) is commonly used to measure reliability.
- Resilience: includes the protection of the network components and the data/information they contain and/or the data transmitted between them.
- Scalability: defines how well the network can adapt to new growth, including new users, applications, and network components.
- Topology: describes the physical layout and the logical way data and information moves between functional components.
- Adaptability: describes how well the network responds to changes in the environment
- Vitality: degree of activity, degree of involvement of participants
- Sustainability: describes how well resources are managed
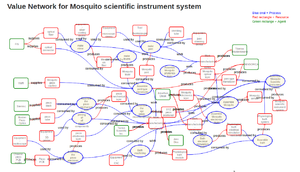
Visualization of OVNs
Diagram representing on of Sensorica OVN's project, "Mosquito Scientific Instrument System":
.